Biomaterials. 2018 Feb;155:64-79. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.10.042. Epub 2017 Oct 29.
Jia T, Choi J, Ciccione J, Henry M, Mehdi A, Martinez J, Eymin B, Subra G, Coll JL.
Abstract
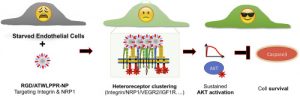
Angiogenesis strongly depends on the activation of integrins, especially integrin αvβ3, and of neuropilin-1 (NRP-1), a co-receptor of VEGFR2. Dual-targeted molecules that simultaneously block both of them are expected have increased anti-angiogenic and antitumor activity. Toward this goal, we generated bifunctional 40 nm-sized silica nanoparticles (NPs) coated with controlled amounts of cRGD and ATWLPPR peptides and studied their affinity, selectivity and biological activity in HUVECs. Sub-nanomolar concentrations of NPs grafted either with ATWLPPR alone or in combination with cRGD exhibit potent and specific antagonist activity against VEGFR2/AKT signaling. However, a 1 nM concentration of the cRGD/ATWLPPR-heteromultivalent particles (RGD/ATW-NPs) also blocks the phosphorylation of VEGFR2 while co-inducing an unexpected long-lasting activation of AKT via IGF-1R/IR-AKT/GSK3β/eNOS signaling that stimulates cell survival and abrogates the intrinsic toxicity of silica-NPs to serum-starved HUVECs. We also showed that their repeated intravenous administration was associated with the proliferation of human U87MG tumor cells engrafted in nude mice and a dilatation of the tumor blood vessels. We present biochemical evidence for the complex cross-talk generated by the binding of the heteromultivalent NPs with αvβ3-integrin and with NRP1. In particular, we show for the first time that such heteromultivalent NPs can trans-activate IGF-1/insulin receptors and exert dose-dependent pro-survival activity. This study demonstrates the difficulties in designing targeted silica-based NPs for antiangiogenic therapies and the possible risks posed by undesirable side effects.