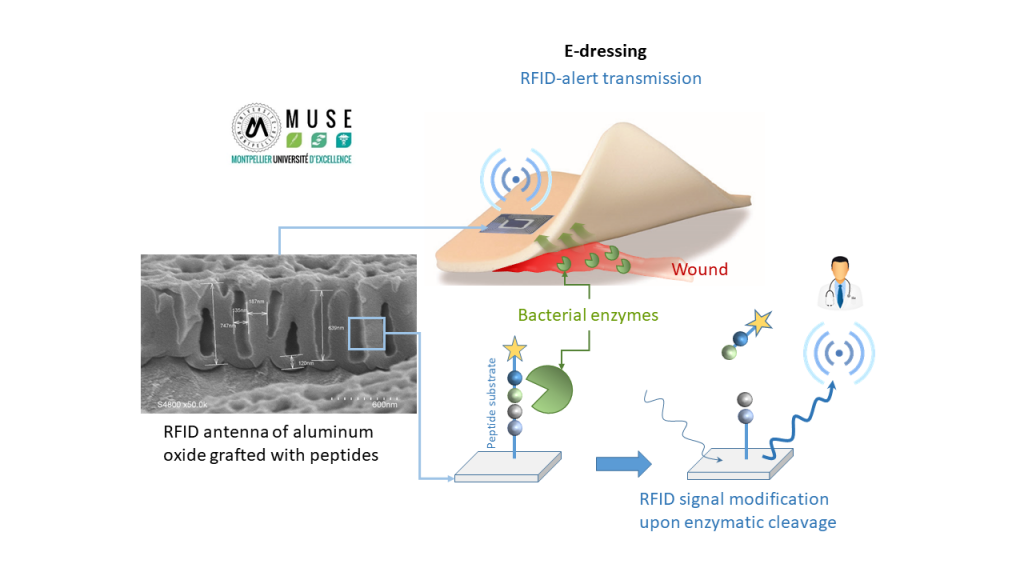
The e-dressing project aims at developing a smart wound dressing able to detect an enzymatic activity and to transmit information by passive RFID (radio frequency identification)

Funding: MUSE research founding
Mar 2018- Feb 2021
E-dressing project
The e-dressing project aims at developing a smart wound dressing able to detect an enzymatic activity and to transmit information by passive RFID (radio frequency identification).
The cost of ineffective treatment of chronic wounds (diabetic foot, leg ulcers…) is estimated to be $20-25 billion annually. Efficient and simple wound diagnostic devices could reduce the complications associated with infection or excessive inflammation being able to target the right therapy, at the right time.
We chose to focus on the design of the RFID device which will be included into the dressing, in contact with the wound exudates. The antenna of RFID device, constituted of porous aluminum oxide, will be grafted by a layer of hybrid material, sensitive to the degradation by bacterial enzymes, virulence markers, or by enzymes related to the inflammation of wounds.
Hybrid material will be composed of hybrid silylated peptides whose sequences will be chosen to be enzyme substrates. Material will be synthesized by sol-gel process and will be degraded specifically by these chosen enzymes.
The first part of the work consists in the design and synthesis of hybrid peptides that will be modified by alkoxysilane groups. They will allow their immobilization by sol-gel process on aluminium oxide substrates.
The second part of the work aims the characterization of the hybrid material (AFM, XPS, SEM…) layer during its degradation. In vitro assays in the presence of isolated enzymes and with relevant bacterial strains will be performed.
The aim of the third part of project is to demonstrate that the degradation of hybrid material by enzymes will generate a detectable modification of electrical signal. Indeed, this electrical variation will impact on the RFID reading and the putative quantification of the targeted enzymes.
At last, the system will be assayed on infected exsudates of patients, collected at Montpellier University Hospital.
E-dressing is multidisciplinary project supported by Montpellier University Site of Excellence which also involves the Institute of Electronics and Systems (IES-team Brice Sorli), the University Hospital of Montpellier (CHU-teams Eric Renard and Luc Teot), Institute Charles Gerhart of Montpellier (ICG-team Ahmad Mehdi) and the Ecole des Mines d’Ales (EAM, team Ingrid Bazin)




