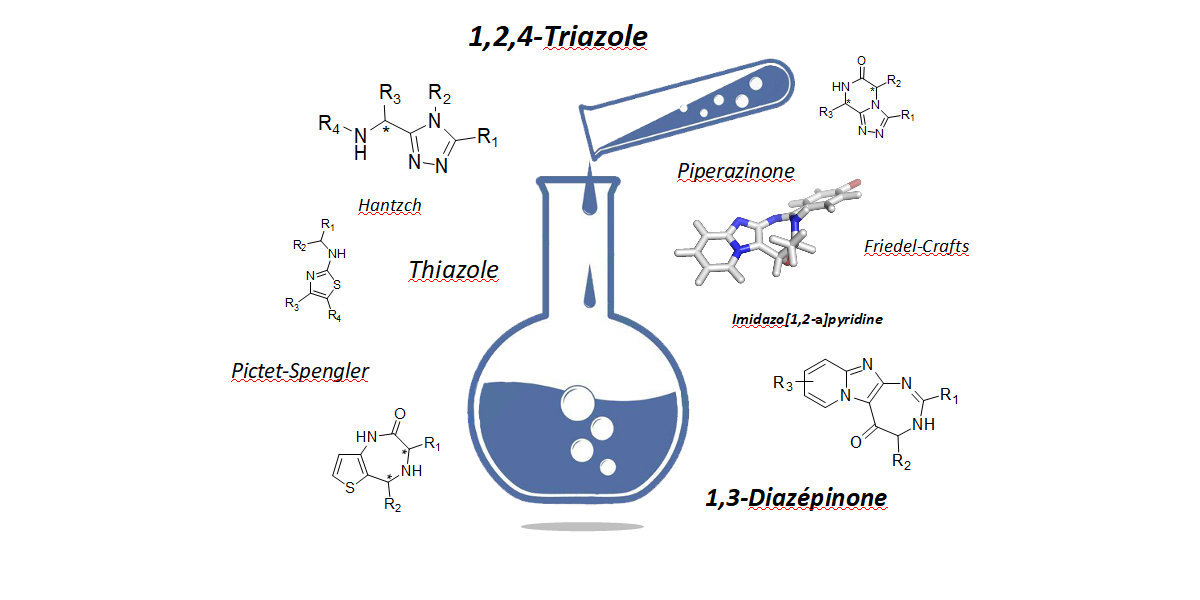
Heterocycles are common structural units in marketed drugs and in medicinal chemistry due to the central role they play in modern drug design. Indeed, heterocycles are useful scaffolds that can be decorated with various substituents in order to modulate lipophilicity, polarity, and hydrogen bonding capacity of molecules. These structural modulations may lead to improved pharmacological, pharmacokinetic, toxicological, and physicochemical properties of drug candidates. Heterocycles are also routinely used as bioisosteres for a variety of functional groups in drug candidates. Therefore, heterocycles represent privileged structures in the drug discovery process.
In order to find new potential lead compounds for therapeutic applications, we develop methodologies to access and structurally modulate heterocycle scaffolds such as [1,2,4]triazoles, diazepines, thiazoles and triazole-ketopiperazines.
CONTACT
Novel thienopyrimidones targeting hepatic and erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium parasites with increased microsomal stability
Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2023, 261, 115873, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115873
P. Lagardère, R. Mustière, N. Amanzougaghene, S. Hutter, M. Casanova, J.-F. Franetich, S. Tajeri, A. Malzert-Fréon, S. Corvaisier, M. Since, N. Azas, P. Vanelle, P. Verhaeghe, N. Primas, D. Mazier, N. Masurier, V. Lisowski
Abstract
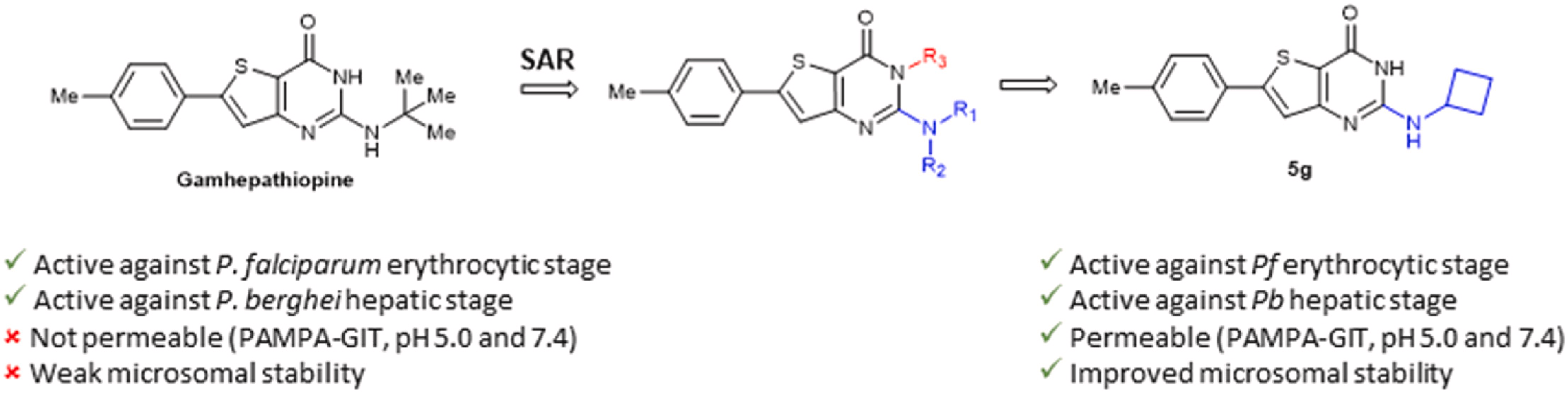
Based on the structure of a previously identified hit, Gamhepathiopine 1, which showed promising antiplasmodial activity, but poor microsomal stability, several strategies were investigated to improve the metabolic stability of the compounds. This included the introduction of fluorine or deuterium atoms, as well as carbocyclic groups. Among the new compounds, the 2-aminocyclobutyl derivative 5g demonstrated enhanced microsomal stability compared to compound 1, while retaining antiplasmodial activity against erythrocytic and hepatic stages of Plasmodium, without significant cytotoxicity against primary hepatocytes.
Novel Hydrazone-Isatin Derivatives as Potential EGFR inhibitors: Synthesis and In vitro Pharmacological Profiling
Arch. Pharm., 2023, 356 (9), 2300244, https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.202300244
M.F. Ahmed, R. El-Haggar, A. H. Almalki, O. Abdullah, M. A. El Hassab, N. Masurier, S. F. Hammad
Abstract
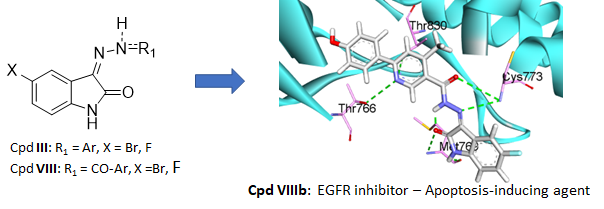
Merging isatin and arylhydrazone moieties constitutes an efficient strategy to access new potential anticancer derivatives. Consequently, 14 hydrazone-isatin derivatives were synthesized and evaluated for their antiproliferative activity against the NCI-60 cancer cell line panel. A kinase assay demonstrated that compound VIIIb inhibited the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which was confirmed by docking studies, molecular dynamics, and binding free energy calculations. Further characterizations showed that this compound possesses drug-likeness properties, showed a significant decrease of the cell population in the G2/M phase and led to a significant increase in early and late apoptosis, comparable to erlotinib. Also, VIIIb increased the expression of caspase-3 and Bax and decreased the expression of Bcl-2, confirming its potential as a new proapoptotic compound.
2,4-Diaryl-pyrimido[1,2-a]benzimidazole derivatives as novel anticancer agents endowed with potent anti-leukemia activity: Synthesis, biological evaluation and kinase profiling
Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2023, 258, 115610, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115610
M. A. Shaldam, D. Hendrychová, R. El-Haggar, V. Vojáčková, T. A. Majrashi, E. B. Elkaeed, N. Masurier, V. Kryštof, H. O. Tawfik, W. M. Eldehna
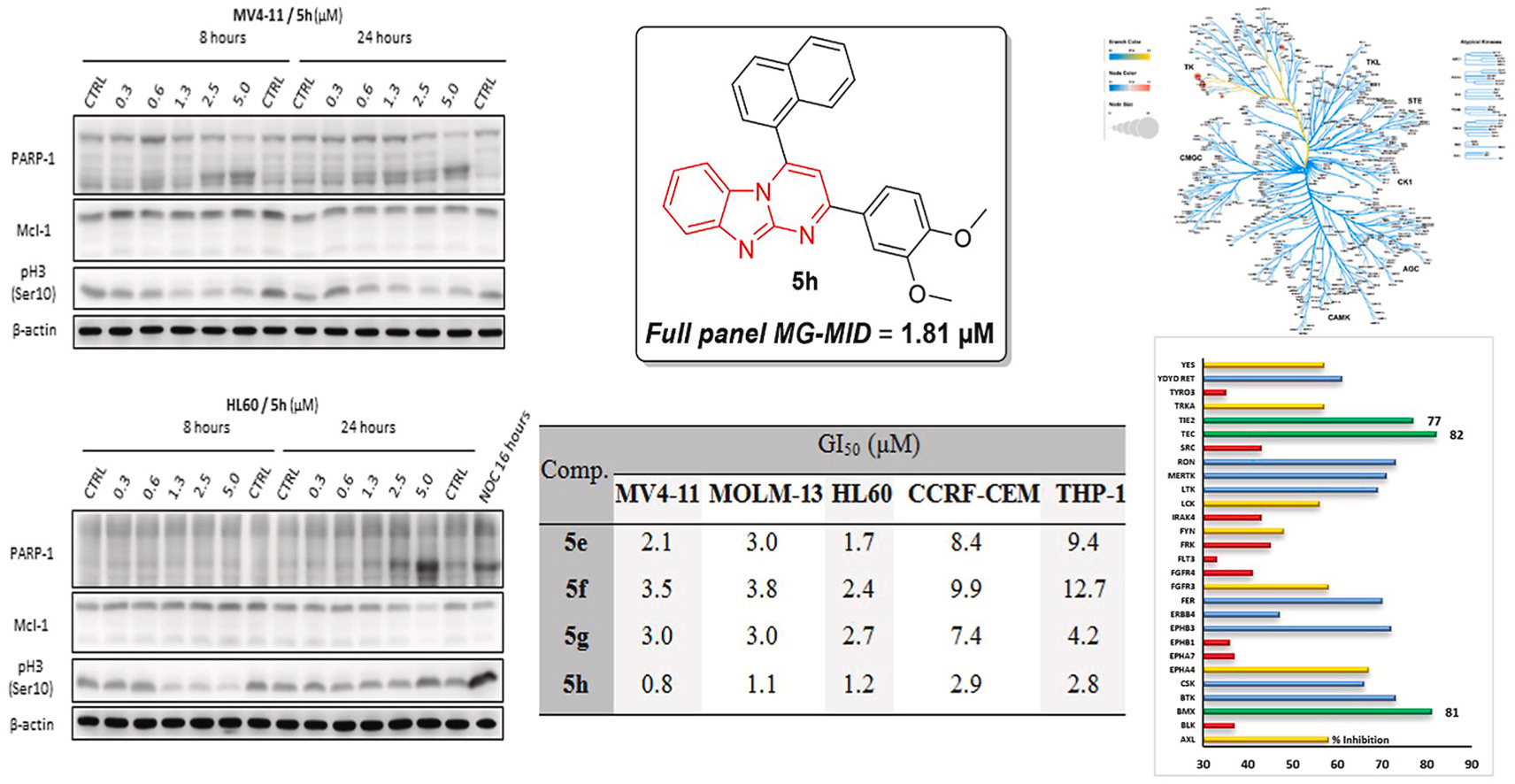
Abstract
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) stands as one of the most aggressive type of human cancer that can develop rapidly and thus requires immediate management. In the current study, the development of novel derivatives of pyrimido[1,2-a]benzimidazole (5a-p) as potential anti-AML agents is reported. The prepared compounds 5a-p were inspected for their in vitro anti-tumor activity at NCI-DTP and subsequently 5h was selected for full panel five-dose screening to assess its TGI, LC50 and GI50 values. Compound 5h showed effective anti-tumor activity at low micromolar concentration on all tested human cancer cell lines with GI50 range from 0.35 to 9.43 μM with superior sub-micromolar activity towards leukemia. Furthermore, pyrimido[1,2-a]benzimidazoles 5e-l were tested on a panel ofhuman acute leukemia cell lines, namely HL60, MOLM-13, MV4-11, CCRF-CEM and THP-1, where 5e-h reached single-digit micromolar GI50 values for all the tested cell lines. All prepared compounds were first tested for inhibitory action against the leukemia-associated mutant FLT3-ITD, as well as against ABL, CDK2, and GSK3 kinases, in order to identify the kinase target for the herein described pyrimido[1,2-a]benzimidazoles. However, the examined molecules disclosed non-significant activity against these kinases. Thereafter, a kinase profiling on a panel of 338 human kinases was then used to discover the potential target. Interestingly, pyrimido[1,2-a]benzimidazoles 5e and 5h significantly inhibited BMX kinase. Further investigation for the effect on cell cycle of HL60 and MV4-11 cells and caspase 3/7 activity was also performed. In addition, the changes in selected proteins (PARP-1, Mcl-1, pH3-Ser10) associated with cell death and viability were analyzed in HL60 and MV4-11 cells by immunoblotting.
Recent advances in aza Friedel–Crafts reaction: strategies for achiral and stereoselective synthesis
Org. Chem. Front., 2023, 10, 1847-1866, https://doi.org/10.1039/D2QO02018A
A. Hadj-Mohamed, N. Masurier
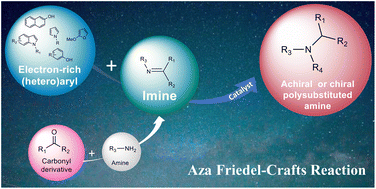
Abstract
The aza-Friedel–Crafts (aza-FC) reaction is a very powerful tool for forming C–C and C–N bonds, based on an acid-catalyzed addition of electron-rich aromatic compounds to imines. This reaction has been particularly useful for synthesizing polysubstituted amines bearing various aromatic groups, as this structural motif is present in many biologically active and pharmacologically relevant compounds. Through representative examples, recent improvements achieved on the aza-FC reaction are presented, classified according to the type of catalyst used. Particular emphasis has been put on the different catalysts used to obtain optically active compounds, as the stereoselective addition of a C(sp2)–H bond to an imine allows access to chiral amines in a completely atom-economical way.
New antiplasmodial 4-amino-thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidines with improved intestinal permeability and microsomal stability
Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2023, 249, 115115, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115115
P. Lagardère, R. Mustière, N. Amanzougaghene, S. Hutter, M. Casanova, J.-F. Franetich, S. Tajeri, A. Malzert-Fréon, S. Corvaisier, N. Azas, P. Vanelle, P. Verhaeghe, N. Primas, D. Mazier, N. Masurier, V. Lisowski
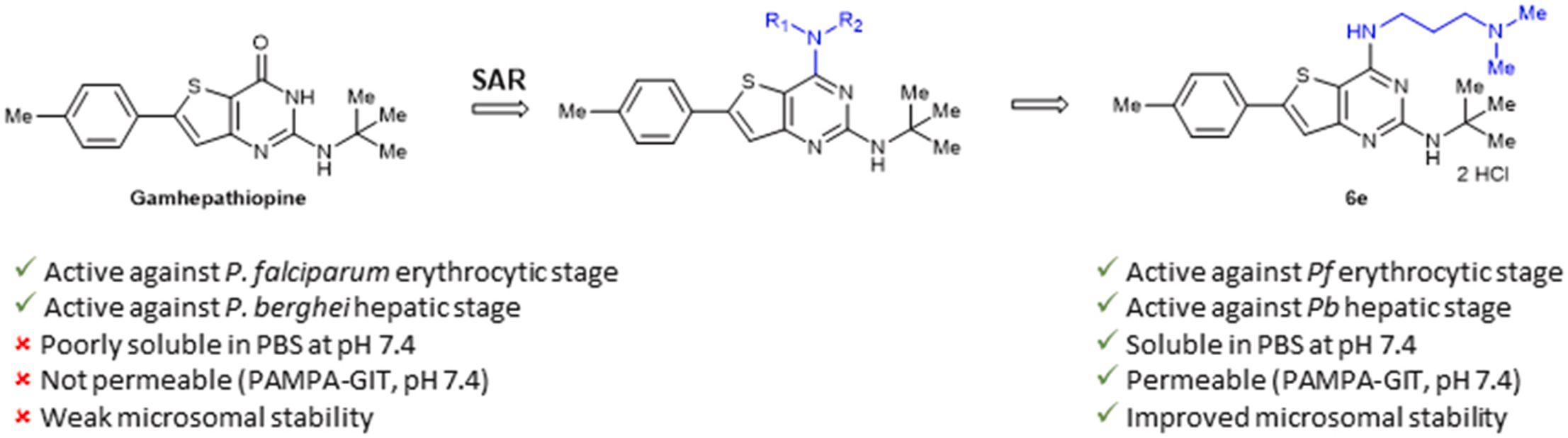
Abstract
The increasing number of Plasmodium falciparum strains resistant to current treatments justifies the urgent need to discover new compounds active on several stages of the parasite development. Based on the structure of Gamhepathiopine, a 2-tert-butylaminothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one previously identified for its dual activity against the sexual and asexual stages of P. falciparum, 25 new 4-amino-substituted analogues were synthesized and evaluated on the erythrocytic and hepatic stages of Plasmodium. A promising compound, N2-(tert-butyl)-N [4]-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-6-(p-tolyl)thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine-2,4-diamine, showed improved physicochemical properties, intestinal permeability (PAMPA model) and microsomal stability compared to Gamhepathiopine, while maintaining a good antiplasmodial activity on the erythrocytic stage of P. falciparum and on the hepatic stage of P. berghei.
3-Substituted-2,3-Dihydrothiazole as a Promising Scaffold to design EGFR Inhibitors
Bioorg. Chem., 2022, 129, 106172, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106172
R. El-Haggar, S. F. Hammad, R. I. Alsantali, M. M. Alrooqi, M. A. El Hassab, N. Masurier, M. F. Ahmed
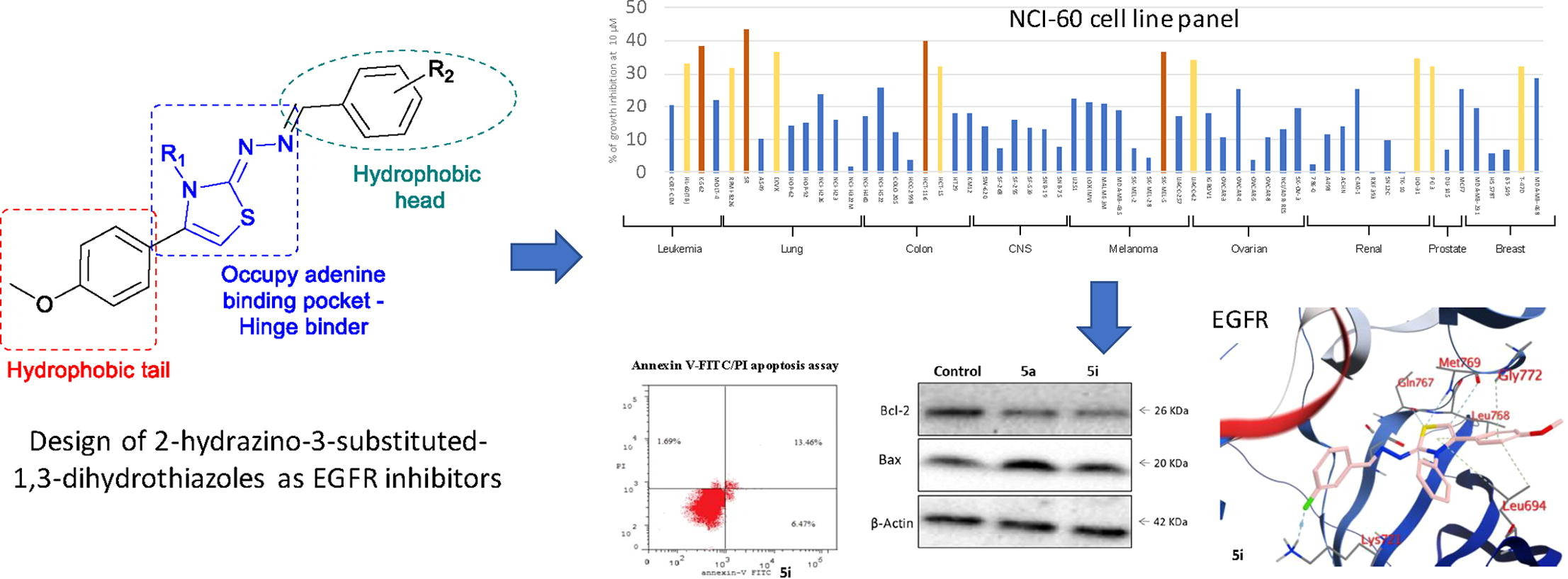
Abstract
The overexpression of EGFR has been recognized as the driver mechanism in the development of several human malignancies and the clinical use of EGFR inhibitors currently constitutes the standard of care for a wide range of malignancies, including colorectal cancer. However, the clinical efficacy of EGFR targeted inhibitors is limited by the development of intrinsic or acquired resistance, requiring the discovery of new compounds with different structural characteristics from those already developed. In this context, we explored the replacement of the aminoquinazoline pharmacophore of several FDA-approved EGFR inhibitors by its bioisosteric hydrazinothiazole moiety. A series of 14 new compounds were designed, synthesized, and evaluated as potential EGFR inhibitors. Compound 5i was active against 12 different cell lines in the NCI-60 cell line panel and showed an IC50 of 6.9 ± 0.013 µM against HCT-116 cells, with no significant toxicity against normal human fibroblasts (WI-38). Further studies showed that this compound showed submicromolar activity against EGFR and was able to induce tumor cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis. Additionally, docking experiments, molecular dynamics and binding free energy calculations were performed and confirmed the potential of 2-hydrazino-2,3-dihydrothiazole derivatives as new EGFR inhibitors.
Synthesis of antiplasmodial 2-aminothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one analogues using the scaffold hopping strategy
Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2022, 241, 114619, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114619
R. Mustière, P. Lagardère, S. Hutter, V. Dell’Orco, N. Amanzougaghene, S. Tajeri, J.-F. Franetich, S. Corvaisier, Marc Since, A. Malzert-Fréon, N. Masurier, V. Lisowski, P. Verhaeghe, D. Mazier, N. Azas, P. Vanelle, N. Primas
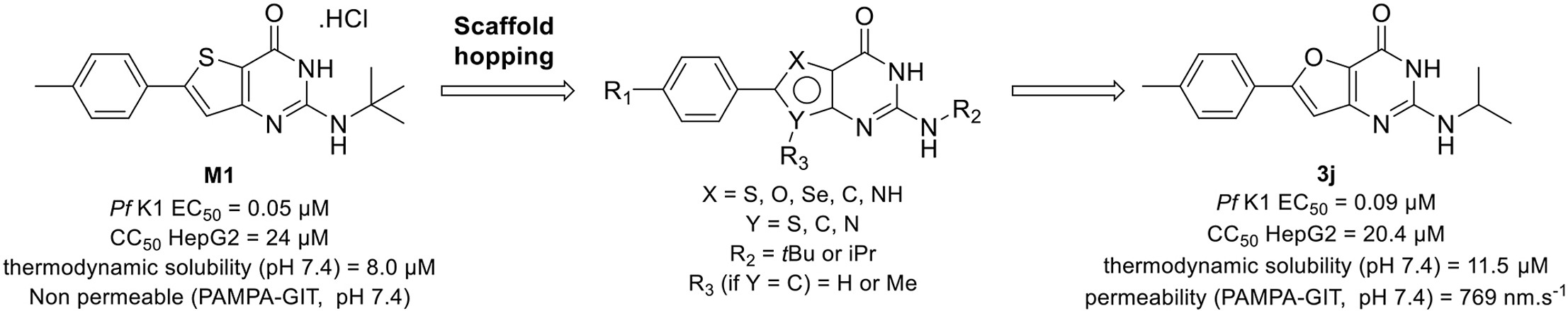
Abstract
Gamhepathiopine (also known as M1), is a multi-stage acting antiplasmodial 2-tert-butylaminothieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one hydrochloride that was first described in 2015. The development of this compound is limited by poor microsomal stability, insufficient aqueous solubility and low intestinal permeability. In order to obtain new optimized derivatives, we conducted a scaffold hopping strategy from compound M1, resulting in the synthesis of 20 new compounds belonging to six chemical series. All the compounds were tested on the K1 multi-resistant strain of Plasmodium falciparum and the human HepG2 cell-line, to evaluate their antiplasmodial activity and their cytotoxicity. Analogues’ biological results also highlighted the mandatory presence of a heteroatom at position 5 of the thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one moeity for the antiplasmodial activity. However, modifications at position 7 were detrimental for the antiplasmodial activity. We identified furane bioisostere 3j as a promising candidate, showing good blood stage antiplasmodial activity, better water solubility and highly improved intestinal permeability in the PAMPA assay.
4-Substituted Thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidines as Dual-Stage Antiplasmodial Derivatives
Pharmaceuticals, 2022, 15, 820, https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070820
P. Lagardère, R. Mustière, N. Amanzougaghene, S. Hutter, J.-F. Franetich, N. Azas, P. Vanelle, P. Verhaeghe, N. Primas, D. Mazier, N. Masurier, V. Lisowski
Abstract
A novel series of 2-thioacetamide linked benzoxazole-benzamide conjugates 1–15 was designed as potential inhibitors of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2). The prepared compounds were evaluated for their potential antitumor activity and their corresponding selective cytotoxicity was estimated using normal human fibroblast (WI-38) cells. Compounds 1, 9–12 and 15 showed good selectivity and displayed excellent cytotoxic activity against both HCT-116 and MCF-7 cancer cell lines compared to sorafenib, used as a reference compound. Furthermore, compounds 1 and 11 showed potent VEGFR-2 inhibitory activity. The cell cycle progression assay showed that 1 and 11 induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase, with a concomitant increase in the pre-G1 cell population. Further pharmacological studies showed that 1 and 11 induced apoptosis and inhibited the expression of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL proteins in both cell lines. Therefore, compounds 1 and 11 might serve as promising candidates for future anticancer therapy development.
Thioacetamido Linker as Potential Anti-proliferative Agents, VEGFR-2 Inhibitors and Apoptotic Inducers
Enzym. Inhib. Med. Ch., 2022, 37 (1), 1587-1599, https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2022.2081844
I.H. Eissa, R. El-Haggar, M.A. Dahab, M. F. Ahmed, H. A. Mahdy, A. S. Khalifa, A. Elwan, N. Masurier, S. S. Fatahala
Abstract
A novel series of 2-thioacetamide linked benzoxazole-benzamide conjugates 1–15 was designed as potential inhibitors of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2). The prepared compounds were evaluated for their potential antitumor activity and their corresponding selective cytotoxicity was estimated using normal human fibroblast (WI-38) cells. Compounds 1, 9–12 and 15 showed good selectivity and displayed excellent cytotoxic activity against both HCT-116 and MCF-7 cancer cell lines compared to sorafenib, used as a reference compound. Furthermore, compounds 1 and 11 showed potent VEGFR-2 inhibitory activity. The cell cycle progression assay showed that 1 and 11 induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase, with a concomitant increase in the pre-G1 cell population. Further pharmacological studies showed that 1 and 11 induced apoptosis and inhibited the expression of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL proteins in both cell lines. Therefore, compounds 1 and 11 might serve as promising candidates for future anticancer therapy development.
Thienopyrimidine: A Promising Scaffold to Access Anti-Infective Agents
Pharmaceuticals, 2022, 15(1), 35, https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010035
P. Lagardère, C. Fersing, N. Masurier, V. Lisowski
Abstract
Thienopyrimidines are widely represented in the literature, mainly due to their structural relationship with purine base such as adenine and guanine. This current review presents three isomers—thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidines, thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidines and thieno[3,4-d]pyrimidines—and their anti-infective properties. Broad-spectrum thienopyrimidines with biological properties such as antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic and antiviral inspired us to analyze and compile their structure–activity relationship (SAR) and classify their synthetic pathways. This review explains the main access route to synthesize thienopyrimidines from thiophene derivatives or from pyrimidine analogs. In addition, SAR study and promising anti-infective activity of these scaffolds are summarized in figures and explanatory diagrams. Ligand–receptor interactions were modeled when the biological target was identified and the crystal structure was solved.








